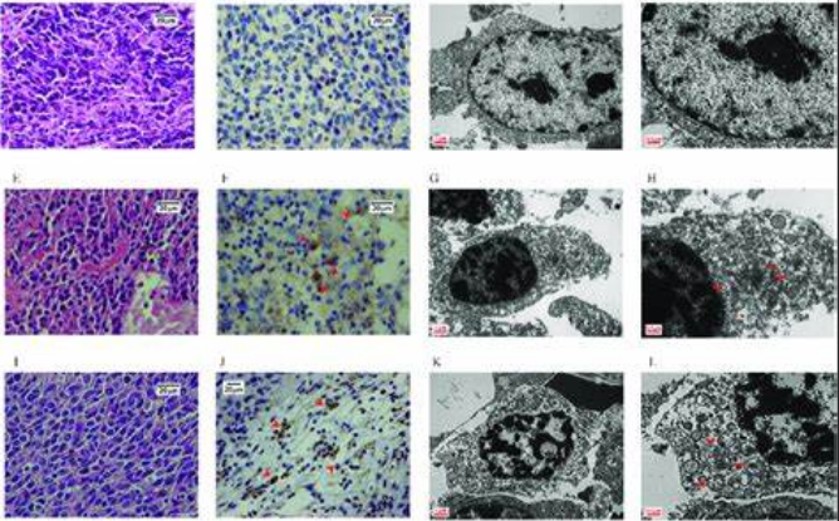
In the realm of biomedical research, animal models play a pivotal role in elucidating the mechanisms of diseases and testing potential therapies. Among the diverse range of mouse models available, the BALB/c-hBCMA model has emerged as a promising tool for investigating human diseases. This article explores the significance of the BALB/c-hBCMA mouse model in advancing medical research and highlights its potential applications.
Understanding the BALB/c-hBCMA Mouse Model
The BALB/c-hBCMA mouse model is derived from the BALB/c strain, a widely used inbred mouse strain known for its susceptibility to a variety of diseases. The model incorporates the human B-cell maturation antigen (hBCMA) gene, which is implicated in multiple myeloma, a form of blood cancer. By expressing the hBCMA gene in a BALB/c background, researchers can study the effects of this specific gene on disease development and progression.
- Investigating Multiple Myeloma
Multiple myeloma is a complex and heterogeneous disease that remains challenging to treat effectively. The BALB/c-hBCMA mouse model provides researchers with a valuable tool to delve into the mechanisms underlying this malignancy. By mimicking the expression of hBCMA observed in human multiple myeloma patients, this model enables the investigation of tumor growth, metastasis, and response to various treatment strategies. Researchers can evaluate the efficacy of novel therapeutics, including targeted agents and immunotherapies, in a more clinically relevant context.
- Immunological Research
The BALB/c-hBCMA mouse model also holds immense potential for studying the immune system. The hBCMA gene plays a crucial role in B-cell maturation and differentiation. By introducing this gene into the BALB/c background, researchers can explore the impact on immune cell development and function. This model can shed light on immune responses, such as antibody production and immune cell activation, offering valuable insights into autoimmune diseases, vaccine development, and immunotherapy approaches.
- Precision Medicine and Drug Development
In the era of precision medicine, the BALB/c-hBCMA mouse model serves as a valuable tool for preclinical drug development. Researchers can utilize this model to evaluate the safety and efficacy of potential therapeutics targeting hBCMA, such as monoclonal antibodies, small molecules, or gene therapies. The ability to assess drug candidates in a genetically engineered mouse model closely resembling human disease enhances the accuracy and predictive value of preclinical studies, facilitating the translation of discoveries into clinical applications.
- Personalized Cancer Treatment
The BALB/c-hBCMA mouse model’s unique characteristics offer potential for personalized cancer treatment strategies. Researchers can use this model to develop patient-derived xenograft (PDX) models by engrafting human multiple myeloma cells into immunodeficient BALB/c-hBCMA mice. These PDX models provide an opportunity to evaluate individual tumor responses to different treatments, allowing clinicians to tailor therapies to specific patients based on their tumor’s characteristics. This personalized approach holds promise for improving patient outcomes and reducing treatment-related toxicities.
Future Directions and Conclusion
The BALB/c-hBCMA mouse model has opened up new avenues for medical research, particularly in the fields of oncology, immunology, and drug development. As researchers continue to investigate the hBCMA gene’s role and its implications for human health, this model will undoubtedly contribute to advancements in our understanding of diseases and the development of innovative therapeutic strategies.
With its ability to mimic human disease characteristics, the BALB/c-hBCMA mouse model offers a powerful tool for preclinical research, bridging the gap between laboratory findings and clinical applications. Further advancements, including the incorporation of additional genetic modifications and the refinement of experimental techniques, will continue to enhance the model’s utility.
As the scientific community progresses, collaborations and knowledge-sharing among researchers utilizing the BALB/c-hBCMA mouse model will facilitate faster discoveries and promote the development of novel treatments. The BALB/c-hBCMA mouse model stands as a testament to the ingenuity and dedication of researchers striving to improve human health through innovative and translational research approaches.
In summary, the BALB/c-hBCMA mouse model provides a valuable platform for investigating multiple myeloma, understanding immune responses, advancing drug development, and personalizing cancer treatments. This model’s potential is far-reaching, and its continued utilization in medical research will undoubtedly pave the way for groundbreaking discoveries and improved patient outcomes.